class Stack():
def __init__(self):
self.data=[]
def add(self,value:str):
self.data.append(value)
def pop(self):
if len(self.data)>0:
return self.data.pop()
else:
return None
def read(self):
if len(self.data)>0:
return self.data[-1]
else:
return None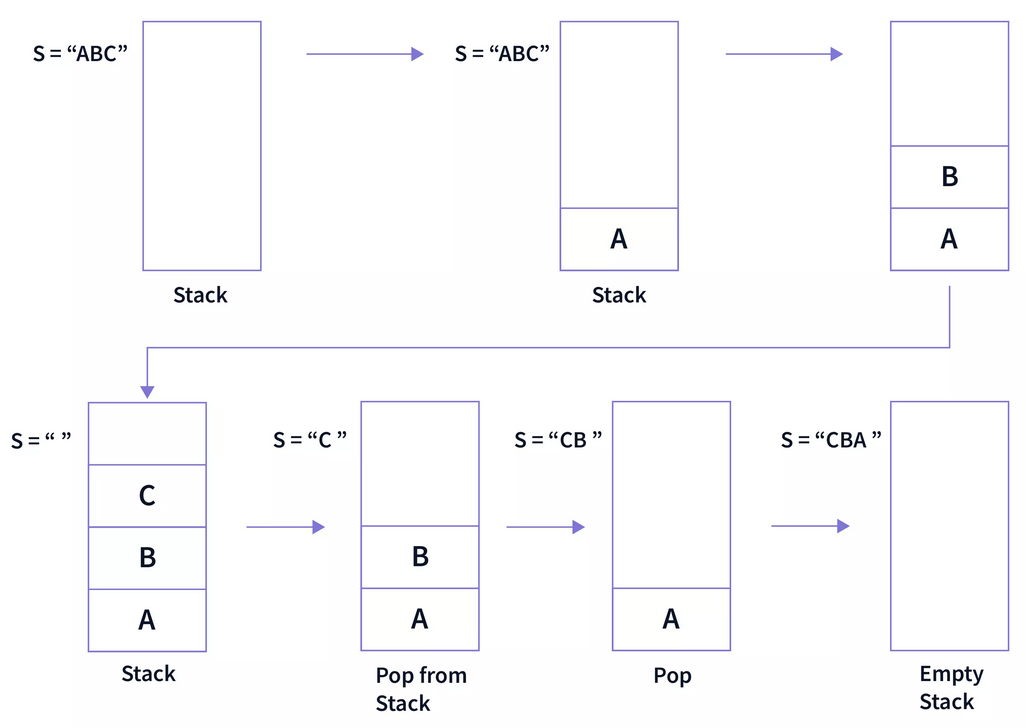
1. Question 1 to 3: simple scenarios
1.1 Call Centre Callers
If you were writing software for a call center that places callers on hold and then assigns them to “the next available representative,” would you use a stack or a queue?
- Queue
1.2 stack: push, pop & read
If you pushed numbers onto a stack in the following order: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and then popped two items, which number would you be able to read from the stack?
- 4: 5 and 6 are popped.
1.3 queue: enque, deque & read
If you inserted numbers into a queue in the following order: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and then dequeued two items, which number would you be able to read from the queue?
- 3: 1 and 2 dequed.
2. Question 4: Use stack to reverse a string
Write a function that uses a stack to reverse a string. (For example, “abcde” would become “edcba”.) You can work with our earlier implementation of the Stack class.
4.1 Psuedo-Code Solution
for-loop a-to-e: add “abcde” to stack viaadd().output =
whileread()isTrue,pop()andappend()to output list i.e. e-to-a.
4.2 Create Stack() class
4.3 Use Stack instance to reverse a string
tony_stack = Stack()
input_string = "abcde"
listify = lambda string: [char for char in string]
# add string into stack
# for char in listify(input_string):
# just realised I dont need to convert string
# to list because its an iterable... oops.
for char in input_string:
tony_stack.add(char)
print(f"{char} added: {tony_stack.data!r}")
# pop string out of stack
reversed_string = ''
while tony_stack.read():
reversed_string+= tony_stack.pop()
print(reversed_string)a added: ['a']
b added: ['a', 'b']
c added: ['a', 'b', 'c']
d added: ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
e added: ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
e
ed
edc
edcb
edcba