1. What are Constants?
Two Types of Constants:
- Named:
- has identifier, by placing attribute
constadjacent to object type: const double gravity1;: compilation error: const variables must be initializedconst double gravity2{9.8};: ok
- has identifier, by placing attribute
- Literals:
- no identifier
5;1.2;"Hello world!"
2. What are Constant Expressions?
The standard defines a constant expression:
- which is an expression that must be evaluatable at compile-time
Containing the following:
- Literals (e.g.
5,1.2) - Most operators with constant expression operands (e.g.
3 + 4,2 * sizeof(int)). - Const integral variables with a constant expression initializer (e.g.
const int x { 5 };)- This is a historical exception,
constexprvariables are preferred (in modern C++).
- This is a historical exception,
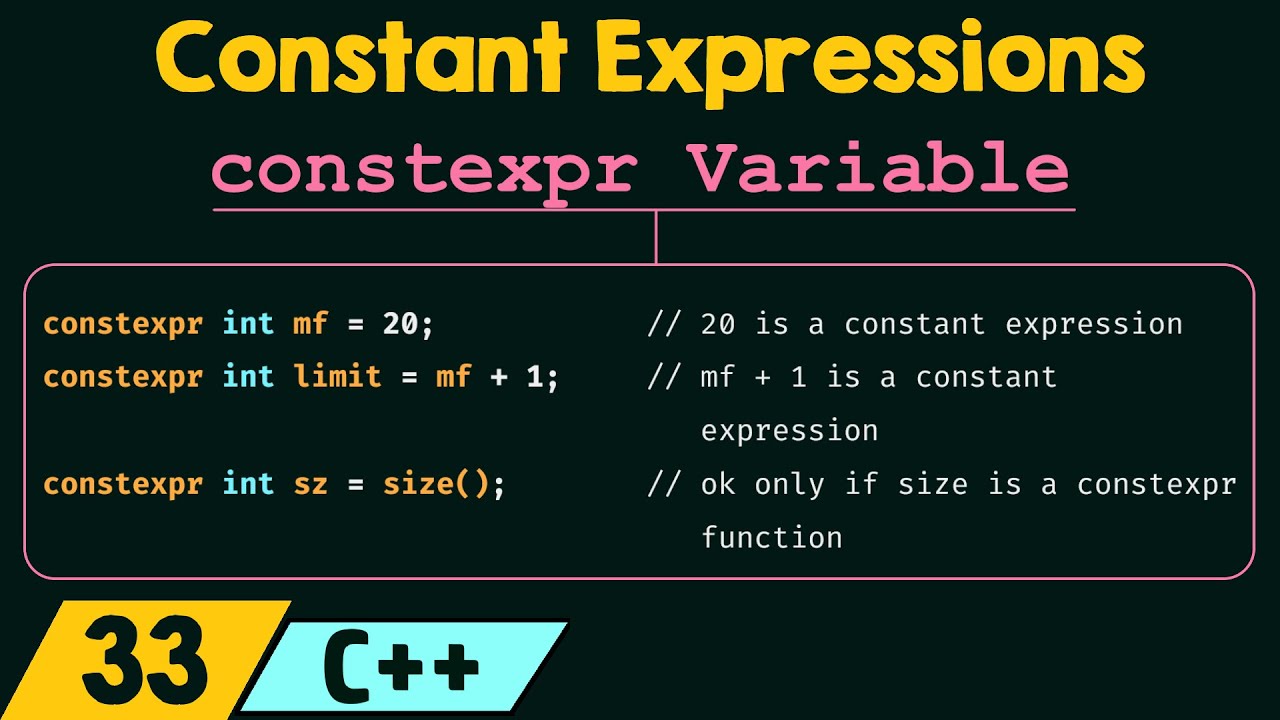
- Constexpr variables (future topic “Constexpr variables”).
- Constexpr function calls with constant expression arguments (future topic “Constexpr functions”).
3. Quiz Constants
For each statement, identify:
- Whether the initializer is a constant or non-constant expression.
- Whether the variable is a constant or non-constant expression.
| Qn | C++ Statement | Initializer | Variable |
|---|---|---|---|
| a) | char a { 'q' }; |
q (const)- a literal |
a (non-const)const keyword unused |
| b) | const int b { 0 }; |
0 (const)- a literal |
b (const)- const int variable - with const express initializer 0 |
| c) | const double c { 5.0 }; |
5.0 (const)- a literal |
c (non-const)- non-integral variable Note: only const integral variables with a constant expression initializer are compile-time constants |
| d) | const int d { a * 2 };- where char a { 'q' }; |
a*2 (const)- a is non-const as missing const keyword |
d (non-const)- a is non-const exp initializer |
| e) | int e { c + 1.0 };- where const double c { 5.0 }; |
c (non-const)- its a non-integral variable (double) |
e (non-const)- missing const keyword - non-integral initializer |
| f) | const int f { d * 2 };- where const int d { 0 }; |
d (const)- integral const expresssion - with const exp initializer 0 |
f (const)-const integral variable - with const expres init d |
| g) | const int g { getNumber() };- where getNumber returns an int by value |
getNumber() (non-const) |
g (non-const) |
| h) | const int h{}; |
default initializer 0 (const) |
h (const)- integral variable - with const expression init |